chegg what should the x bar and r chart control limits be to meet the cp target ?
What are X Bar S Command Charts?
10 Bar Due south charts often used control chart to examine the process mean and standard deviation over the time. These charts are used when the subgroups have large sample size and South nautical chart provides improve understanding of the spread of subgroup data than range.
Ten bar Due south charts are as well similar to X Bar R Control chart, the basic deviation is that Ten bar S charts plots the subgroup standard deviation whereas R charts plots the subgroup range
Option of advisable command chart is very important in control charts mapping, otherwise concluded upward with inaccurate control limits for the data.
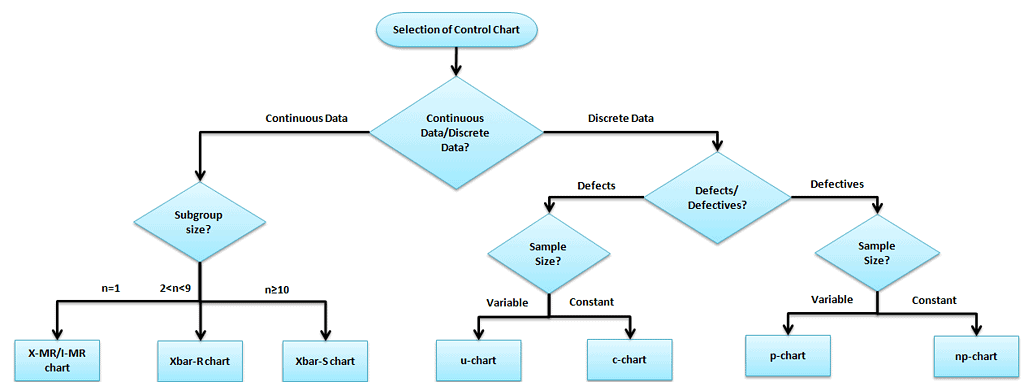
Manually it is very easy to compute X Bar R Control chart, where every bit sigma chart may be difficult due to tedious calculations and big sample size. With big sample size in the subgroup, the standard difference is better measure out of variation than the range because it considers all the data not but minimum and maximum values.
Information technology is actually a 2 plots to monitor the process hateful and the process range (every bit described by standard deviation) over time and is an example of statistical process control. These combination charts helps to sympathize the stability of processes and too detects the presence of special cause variation.
The cumulative sum (CUSUM) and the exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) charts are as well monitors the hateful of the process, but the basic divergence is dissimilar X bar chart they consider the previous value means at each bespeak. Moreover these charts are considered equally a reliable estimate when correct standard deviation exists.
10 Bar South Control Chart Definitions
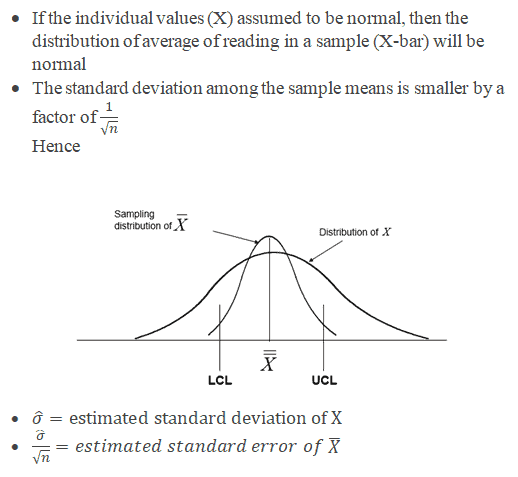
Ten-bar chart:The hateful or boilerplate change in procedure over fourth dimension from subgroup values. The command limits on the Ten-Bar brings the sample's mean and center into consideration.
Due south-nautical chart: The standard deviation of the process over the time from subgroups values. This monitors the process standard divergence (as approximated by the sample moving range)
Utilise X Bar S Control Charts When:
- The sampling process is same for each sample and is carried out consistently.
- When the data is causeless to exist usually distributed.
- The X bar Southward chart to be used when rationally collect measurements in subgroup size is more 10.
- X Bar R chart is to exist considered if the subgroup size is between ii and 10 observations (for I-MR chart the subgroup size is one just).
- When the collected data is in continuous (ie Length, Weight) etc. and captures in time club
How to Interpret the X Bar South Command Charts
- To correctly interpret 10 bar S chart, always examine the Southward nautical chart first.
- The X bar chart command limits are derived from the S bar (average standard deviation) values, if the values are out of command in S chart that means the 10 bar nautical chart command limits are not accurate.
- If the points are out of control in S chart, then finish the procedure. Identify the special crusade and address the issue. Remove those subgroups from the calculations.
- Once the Southward chart is in control, and then review X bar chart and interpret the points against the control limits.
- All the points to be interpret against the control limits but not specification limits.
- If any betoken out of control in 10 bar conversation. Identify the special cause and address the outcome.

Steps to follow for X bar S chart
Objective of the nautical chart and subgroup size
- Determine the objective of the chart and cull the important variables
- Choose the appropriate subgroup size and the sampling frequency
- Shewhart suggested collecting xx to 25 sets of samples with a subgroup size of x and above
Note: To demonstrate an example, nosotros just took subgroup size four in the below example, but it is always recommended to take ten and to a higher place for X bar S chart.
Instance:A packing system monitoring the performance of a packing machine, each container should weigh 35 lb, during Measure phase, project squad performed the procedure adequacy study and identified that the procedure is not capable(less than one sigma). In Clarify phase nerveless 12 sets of container weights with a subgroup size of 4.
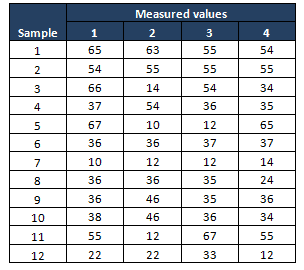
Compute 10 bar and Due south values
- Mensurate the average of each subgroup i.eastward 10 bar, then compute thou average of all X bar value, this will be center line for X bar chart
- Compute the standard deviation of each subgroup, so mensurate grand averages of all standard values ie S bar and this will be the center line for South chart
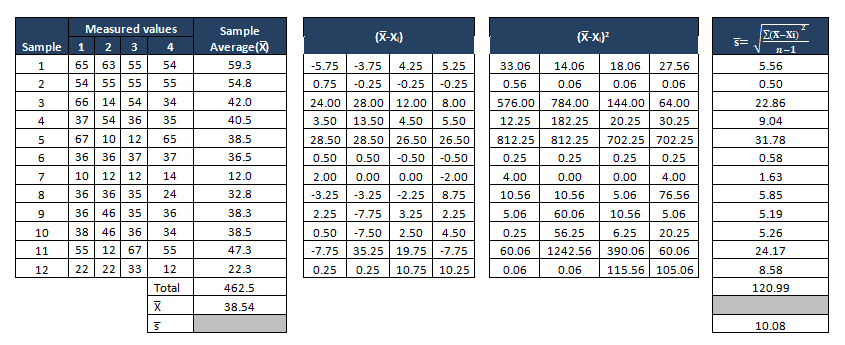
Decide the Command Limits
The outset ready of subgroups are to decide the process mean and standard deviation, these values are to exist consider for creation of control limits for both standard deviation and mean of each subgroup
The process to be in control in the early on stage of the production. Special causes to exist identified if whatever of the points are out of command during initial phase and besides the subgroup has to be removed for adding.
Sometimes in the initial phase information technology would be as well good to have few points out of control on the ten-bar portion. Otherwise, if all the values are within the control limits may be because of slop in the measurement organisation, team won't focus on it. Identify appropriate Measurement System Evaluation (MSE).
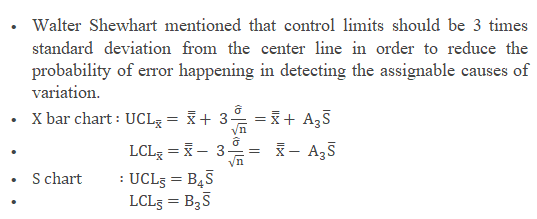
- Where
- 10 is the individual value (data)
- n is the sample size
- Ten bar is the boilerplate of reading in a sample
- South is the standard departure
- S bar is the boilerplate of all the standard deviation.
- UCL is Upper command limit
- LCL is Lower control limit
The below control chart constants are judge values to measure out the control limits for Ten bar Southward chart and other command charts based on subgroup size
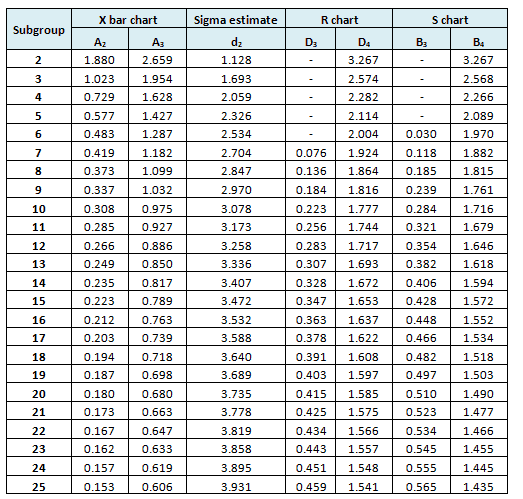
- Refer common factors for various control charts
Example cont: In the above example north=4
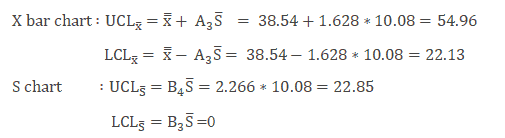
Interpret X bar and S chart
- Plot both 10 bar and South chart and identify the assignable causes
Instance Cont: Utilise the to a higher place values and plot the X bar and Sigma nautical chart
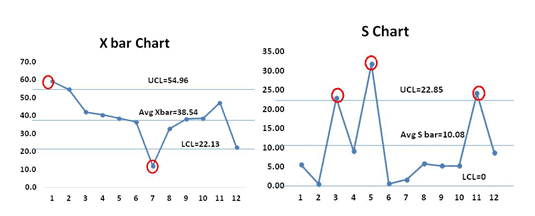
From the both X bar and S charts it is conspicuously evident that virtually of the values are out of control, hence the procedure is not stable
Monitor the process afterward improvement
Once the process stabilizes and control limits are in identify, monitor the process performance over the time.
Example cont: Control Phase- Once the process is improved and matured, team identified the X bar S chart is one the control method in Command programme to monitor the process performance over the fourth dimension period
Following are the measurement values in Command phase of the project
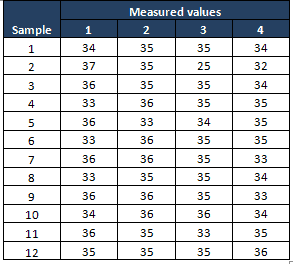
Compute X bar and Sigma
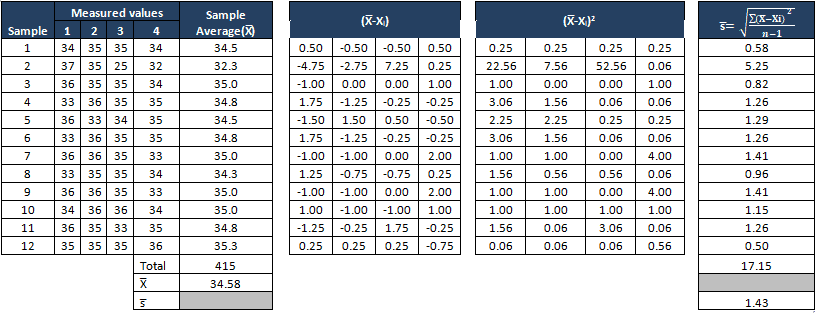
Find the control limits
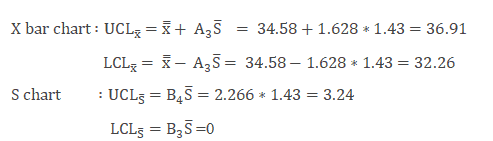
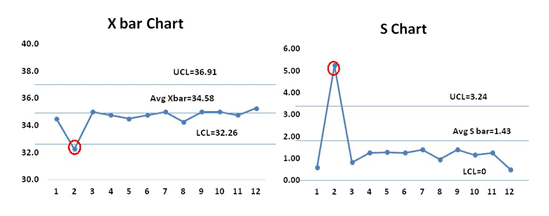
From the both 10 bar and S charts information technology is clearly evident that the procedure is nearly stable. During initial setup at 2nd data set both S chart and X bar chart value are out of control, team has to perform the root cause analysis for the special cause and also the procedure is smoothing out from the information prepare number four. If that continued, the chart would need new command limits from that point.
- Since South nautical chart is in statistical control, calculate the procedure standard deviation

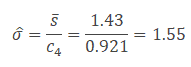
- After the process stabilized, still if any point going out of control limits, it indicates an assignable cause exists in the process that needs to be addressed. This is an ongoing process to monitor the procedure performance.
Important notes on Ten Bar S Control Charts
- A process is "in control" that indicates means of the process is stable and information technology tin can be predictable
- A process is in stable that does non mean it'southward a zero defect procedure.
- Call back to NEVER put specifications on whatever kind of command chart.
- The points on the chart are comprised of averages, not individuals. Specification limits are based on individuals, not averages.
- The operator might take the tendency to non react to a point out control when the indicate is inside the specification limits.
- X bar S nautical chart helps to avert unnecessary adjustments in the process
Ten Bar S Control Chart Videos
carpenterthoulace.blogspot.com
Source: https://sixsigmastudyguide.com/x-bar-s-chart/
Publicar un comentario for "chegg what should the x bar and r chart control limits be to meet the cp target ?"